Meaning of industry 4.0
The term “Industry 4.0” is used for the fourth industrial revolution. This revolution is characterized by the integration of advanced digital technologies into manufacturing and production processes, leading to the creation of smart factories. These technologies include the Internet of Things (IoT), big data analytics, artificial intelligence (AI), cloud computing, and more. Industry 4.0 is transforming various sectors in India, driving efficiency, innovation, and competitiveness.
What is Industry 4.0?
Industry 4.0 refers to the automation and data exchange trend in manufacturing technologies. It encompasses:
IoT: Connecting machines, devices, and systems to collect and exchange data.
Big Data Analytics: Analyzing large data sets to gain actionable insights and improve decision-making.
AI and Machine Learning: Using algorithms to automate processes, predict outcomes, and optimize operations.
Cloud Computing: Storing and accessing data over the internet, enabling remote monitoring and control.
Cyber-Physical Systems: Integrating physical processes with digital systems to create smart environments.
Benefits of Industry 4.0
Cost Reduction
Automation and efficient resource utilization lower production costs. Predictive maintenance reduces equipment downtime and repair costs, while optimized processes minimize waste.
Increased Innovation
Industry 4.0 fosters innovation by integrating new technologies and approaches. It enables rapid prototyping, faster time-to-market, and continuous improvement in products and processes.
Better Decision-Making
Data analytics and real-time monitoring provide valuable insights for decision-making. Businesses can respond quickly to market changes, optimize operations, and improve strategic planning.
Enhanced Customer Experience
Customization and improved product quality lead to higher customer satisfaction. Faster delivery times and responsive service enhance the overall customer experience.
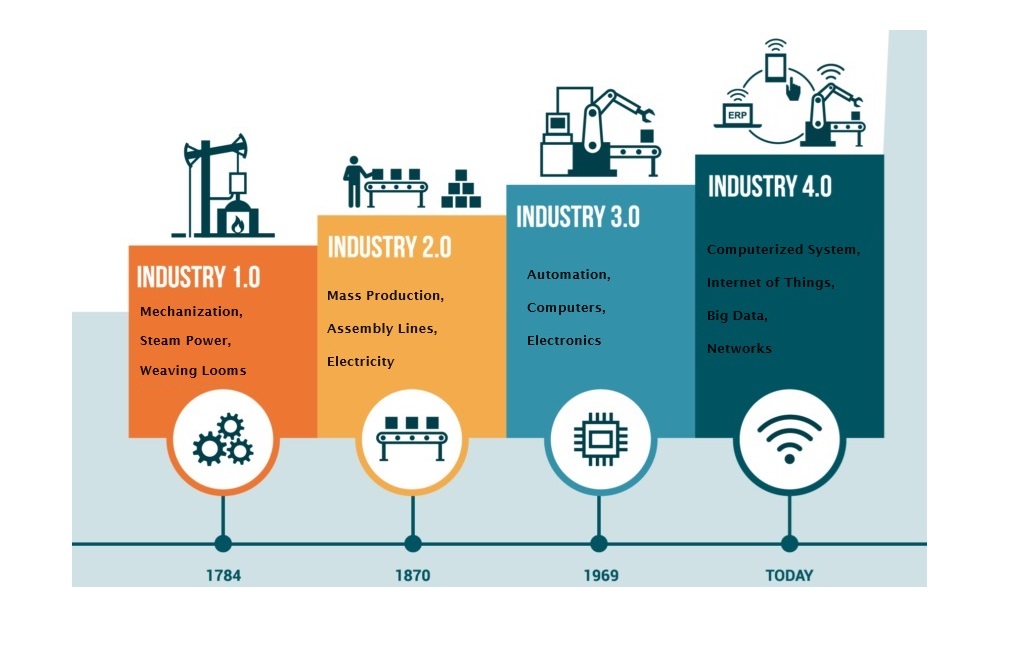
Evolution from Industry 3.0 to Industry 4.0
The shift from Industry 3.0 to Industry 4.0 is primarily marked by the integration of digital technologies into manufacturing processes. While Industry 3.0 focuses on the automation of single machines and processes, Industry 4.0 integrates these machines into a cohesive, digitally connected system.
Compared to the standalone automated systems in Industry 3.0, Industry 4.0’s interconnected and intelligent systems are capable of self-optimization, self-configuration, and even self-diagnosis, leading to higher productivity and flexibility.
The Evolution of Industry 4.0 in India
Since its inception, Industry 4.0 has gradually gained momentum in India. The country’s robust IT sector, coupled with a growing focus on digital transformation, has positioned India as a significant player in the global Industry 4.0 landscape. Key Milestones in India’s Industry 4.0 Journey:
- Adoption of IoT and AI: Indian industries began integrating IoT and AI technologies to enhance productivity, reduce costs, and improve quality. For example, in the automotive sector, companies like Tata Motors and Mahindra & Mahindra implemented IoT solutions for real-time monitoring and predictive maintenance.
- Smart Manufacturing: The concept of smart manufacturing gained traction with companies like Bharat Heavy Electricals Limited (BHEL) and Larsen & Toubro (L&T) adopting advanced automation and robotics to streamline their operations.
- Government Initiatives: The Indian government launched initiatives like the “Make in India” campaign and the National Manufacturing Policy, promoting the adoption of Industry 4.0 technologies. These initiatives aimed to boost manufacturing, create jobs, and enhance global competitiveness.
- Digital Infrastructure: The development of digital infrastructure, including high-speed internet and data centers, facilitated the implementation of Industry 4.0 technologies. This infrastructure is crucial for the seamless exchange of data and remote management of industrial processes.
Impact on Indian Industries
Industry 4.0 has had a profound impact on various sectors in India, transforming the way businesses operate and compete. Here are some notable examples:
1. Automotive Industry: The automotive sector has been at the forefront of adopting Industry 4.0 technologies. Companies use IoT for connected vehicles, AI for autonomous driving, and big data for customer insights. This has led to improved vehicle safety, enhanced customer experiences, and efficient supply chain management.
2. Manufacturing: Smart factories are becoming a reality in India, with manufacturers leveraging automation, robotics, and AI to optimize production. For instance, Bajaj Auto uses AI-powered robots for assembly line tasks, resulting in higher precision and reduced defects.
3. Healthcare: The healthcare industry is utilizing Industry 4.0 technologies for telemedicine, remote patient monitoring, and personalized treatments. AI-driven diagnostic tools help in early disease detection and efficient healthcare delivery.
4. Agriculture: Indian agriculture is embracing precision farming techniques powered by IoT and AI. Farmers use sensors and drones to monitor crop health, optimize irrigation, and increase yield. Companies like Mahindra Agribusiness are at the forefront of this transformation.
5. Energy: The energy sector is adopting smart grid technologies, renewable energy solutions, and AI for predictive maintenance. This has improved energy efficiency, reduced outages, and facilitated the integration of renewable energy sources.
Challenges and Concerns with Industry 4.0
While Industry 4.0 offers undeniable benefits, it also brings noteworthy challenges and concerns that industries must address to harness its full potential effectively.
- Security and Data Privacy: As manufacturing systems become more connected, the risk of cyber threats significantly increases. Companies face challenges in protecting sensitive data from hackers who could potentially seize control of automated systems and production lines.
- Workforce Displacement: The shift towards automation and the use of AI in manufacturing could lead to significant workforce displacement, as machines replace human roles in performing routine tasks.
- Skill Gap: There is a need for a skilled workforce proficient in digital technologies. Upskilling and reskilling programs are essential to bridge this gap.
- Infrastructure: Although digital infrastructure is improving, there is still a need for widespread high-speed internet and reliable connectivity, especially in rural areas.
- Investment: Implementing Industry 4.0 technologies requires significant investment. Small and medium-sized enterprises (SMEs) may struggle to afford these technologies without adequate financial support.
Industry 4.0 Success Stories
Despite these challenges, many companies have successfully adopted Industry 4.0 technologies and have seen substantial improvements in efficiency, productivity, and profitability.
Case Study 1:
A large automotive manufacturer, integrated IoT sensors and AI across its production lines, enabling real-time data analysis and predictive maintenance of equipment. This shift not only reduced downtime by 45% but also increased the overall equipment effectiveness (OEE) by 30%. The ability to predict potential equipment failures before they occurred significantly cut repair costs and optimized the production schedule according to real-time demand and supply data.
Case Study 2:
A textile company, adopted automated robotic systems and machine learning algorithms to sort fabrics and colors, boosting both speed and accuracy in their operations. As a result, production increased by 20%, and the error rate dropped by 60%. Furthermore, the data collected from the automation process allowed the Company to analyze trends and consumer preferences, leading to better inventory management and less waste, showcasing how adaptation and innovation can significantly transform traditional industries.
In the journey through the complexities and innovations of Industry 4.0, it’s clear this revolution is reshaping the manufacturing landscape. By integrating intelligent technologies such as IoT, AI, robotics, and big data analytics, businesses are achieving greater efficiency and productivity. As we look towards the future, staying informed and adaptable will be key to leveraging the opportunities during Industry 4.0. Embracing these technological advances will not only streamline operations but also enhance competitiveness in the global market.

