What is 5s implementation?
- How to start 5s Implementation? 5S Methodology was developed in Japan and it’s a system for organizing spaces so work can be performed efficiently & effectively safely it’s a fundamental tool of Lean Manufacturing
- It’s a system for organizing space so work can be performed efficiently & effectively with safety.
- Now and then it’s also referred to as a good housekeeping practice but both are different things
Benefits of 5S Quality 5s meaning | What does the 5S Stand for? |How To Start 5S Implementation
1. History:
- This methodology was developed in Japan by two gentlemen, Osada, and Hirano who structured a framework for implementing their philosophy.
- Some say that the principles of this Methodology came from Henry Ford.
- Henry Ford used the CANDO system (CANDO stands for Cleaning up,
- Arranging, Neatness, Discipline, and Ongoing Improvement) before the development of this Methodology.
2. Benefits of 5S
- Increase productivity through effectiveness
- Reduction in delays
- Improved
3. Quality
- Improve in Safety
- Set-up times reduced
- Morale & MotivationIncrease
- Lessstress for operators
- Safer work atmosphere
- Improvement in the regular process
4. 5S Meaning| What does the 5S stand for?
- It stands for five Japanese wordsSeiri, Seiton, Seiso, Seiketsu, and Shitsuke.
- English Meaning of the above Japanese words are
- (1S) Seiri → Sort or Tidiness
- (2S) Seiton → Set In Order or Orderliness
- (3S) Seiso → Shine (Clean) or Cleanliness
- (4S) Seiketsu → Standardize or Standardization
- (5S) Shitsuke → Sustain or Discipline
5. how to start 5s implementation?
- Now we will see the implementation of 5S step by step.
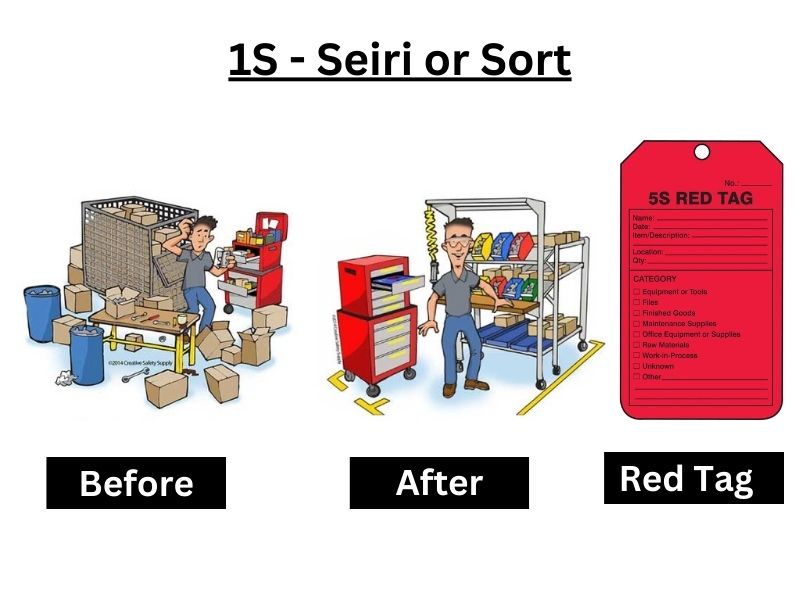
(1) 1S-Seiri or Sort
- The first step is to Sort in this Methodology.
- ” Sorting” means sorting everything in each work area that we need and what we do not need.
- Sort means removing nonessential items or materials from a workspace.
- Keep only what’s actually needed every day from the workspace.
- Materials, equipment, instruments, or any things that aren’t constantly- used should be moved to a separate, common warehouse area called Red Tag
Zone. - Items that aren’t used should be removed or recycled.
- Please don’t keep anything in your plant just because it might be used in the future.
- The whole team should spend a few hours going through the entire area (inside closets, under and behind machines. Everyplace!!!)
- All obvious scrap should be put in the scrap area/ box
- All unidentified things should be put in the “ Red label”/ quarantine area.
- Only items that are needed should remain.
Steps for Sorting
- Cleaning
- Classifying
- AssignResponsibility
- Red Tagging of nonessential things
- Recycling or Reassignment of things arrived in Red Tag Zone.
- For a better understanding of how the below picture of the Before-After comparison of Work Place and the Red Tag
5S Exemplifications
(2) 2S-Seiton or Set In Order
- Set in order is for organizing the items or materials at the plant.
- “ DefinePlace for Everything and Put Everything in its place”
- We can use a systematized plant more efficiently and effectively
- To arrange all necessary items for the economy of movement.
- Put things as per the frequency of use.
- Provide a safe warehouse – heavy items at a low rank, light items at a height.
- If any item is missing also we can fluently find out it
Basic Principles of Set-in Order
- The items that are used really constantly should be kept nearer to where they’re used.
- Items that are used really multiple times should be kept far compared to constantly used things.
- After completion of work keep things in their defined place.
- If several things are used together, also store them together.
- For illustration, a welding rod is used with a welding machine also both should be kept together.
- Store things in a place where people can fluently find
- Identify all items ( including fixtures, gauges, tools, jigs, molds, etc.) and mark identification symbols on them so we can fluently identify and return
them to their identified warehouse place. - For better understanding refer to the below picture of the sort in order.

5S Housekeeping
(3) 3S-Seiso or Shine (cleaning)
- After Sort and Set In Order, the plant requires regular
- Shine is used for regular cleaning of the plant, tools, and equipment
- Cleanliness makes defects easier to detect.
- Better client satisfaction
- Creates a better working atmosphere
- It isn’t just the job of a housekeeper, it’s everyone’s responsibility
- Every plant should have a person, or group, assigned to clean that area.
- The best approach is that those who work in a plant are also responsible for cleaning that area.
(A) Cleaning is an ongoing process
- Define and document
- Decide Who, What, When, Where, How, etc …
- Who’s responsible for cleaning
- What needs to be cleared and where
- When it’ll be done
- How is it to be done and which tools demand
- For better clarity related to the below picture in which we can fluently see the comparison of the plant before and after cleaning.

(4) 4S-Seiketsu or Standardize
- After completion of Shine or Clean, Standardize will come.
- Standardizing means documenting each necessary process or activity.
- Standardizing can turn Good Practices into Good Habits.
- By developing standards for process, all person knows what to do, how to do it, when to do it, where to do it, etc.
- Give awareness about standardizing to all persons.
- It’ll help them to remember the new standards and it encourages them to do the same.
- We can use tags, symbols, posters, and banners for standardization.
(A) How do we Standardise?
- Document standard ways of working ( SOPs),. Process Flow Diagram or Flow Chart
- Standardize labeling, signage, and Flow
- Audits
(B) Standard Work
- Document the current agreed way of doing a process
- Provides a baseline for improvement
- Reduces variation between people/ shifts
(C) Standardized flow and Signage
- Common methodologies to show where the work enters and leaves the cell.
- Standard methodologies for identifying components and tool places
(D) 5S Audit
- Independent audit of an area
- Capture current state – Use color photos

Document
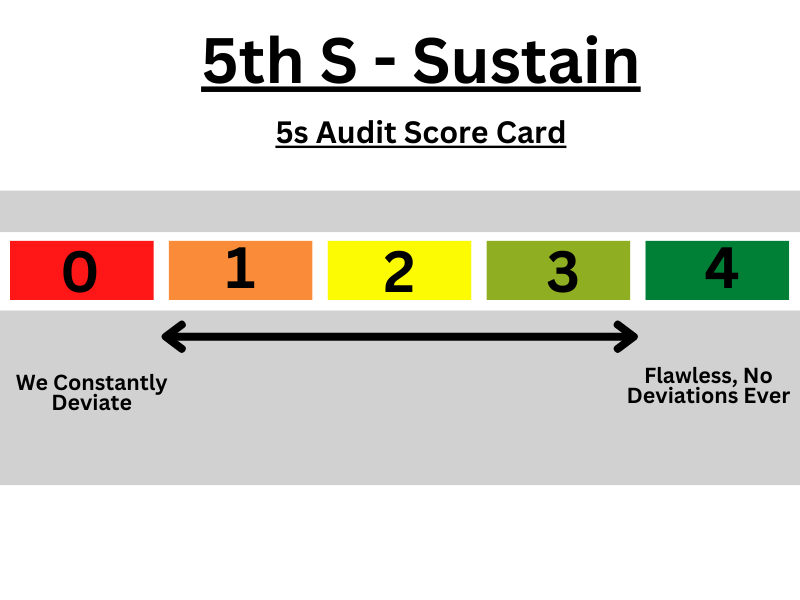
(5) 5S-Shitsuke or Sustain
- Sustain needs to maintain 5S within the plant or work pace.
- Keep a record of progress with evaluations, communication, and training-related activity.
- Assign continuing responsibility.
- Sustain keeps watch on ongoing training activity and maintains the Established System.
- Maintaining Audits
- Maintaining cleaning
- Making it “ A Way of Life”.
you can also avail 5s Training from us
Top Management’s Support needed to Sustain
- We can sustain our commitment to the 5S methodology in our industry with the help of Top management’s support.
- Top Management should be involved in these activities similar as
- Conducting inspections on a random basis for checking the sustenance of the system
- Establish a proper communication channel from top to bottom and bottom to top.
- Provides training to workers.
- Participation in promotional events at the plant.
- What Is 5s System & why 5s fail What Is 5s System Honest Video, how to start 5s implementation?
- How can you beat covid-19 by implementing 5S Japanese Practice
- How to Reduce Inventory, Inventory Management Tool & Tactics
- What Is Kaizen, What Is Kaizen With Example, non-value added activity, Kaizen Muda
- One Point Lesson | One point lesson types & example |TPM one point lesson | OPL explain
- Learn The 7 Wastes Of Lean The 7 Wastes of Lean for Frontline Kaizen -Lean Manufacturing Training
- Overall Equipment Efficiency What Is OEE – Overall Equipment Effectiveness Solution
- What is Lean Manufacturing | Lean tool crash course | Lean Manufacturing in 5 min | Lean in Hindi
- 8 Wastes of Lean, lean manufacturing
- Lean Implementation, the benefit of Lean, lean practice, and how to implement lean tools