Top lean Manufacturing – Lean Operation Tools
- Top lean Tools are the methodical and scientific approaches to the problem- working.
- Spare Tools are also used for relating and barring waste from the system or process.
- These tools are veritably important to apply Lean Manufacturing culture in the plant.
The list of top lean tools are
- Kaizen
- Single Piece Flow
- Jidoka
- Poka Yoke
- Visual Management
- Kanban
- 8 lean Wastes
- Six Big Losses
- Smart Goal
- Heijunka
- Just in time
- Takt time
- Bottleneck Analysis
- Andon
- Gemba
- Hoshin Kanri
- Overall Equipment Effectiveness (OEE) – Also watch video on overall equipment Efficiency
- Cellular Manufacturing
- Total Productive Management (TPM)
- Total Quality Management (TQM)
- Value Stream Mapping (VSM Study)
- Single Minute Exchange of Dies (SMED) – watch video on SMED
- Crucial Performance Pointers (KPIs)
- 5S Methodology
- Standardize work
- PDCA cycle
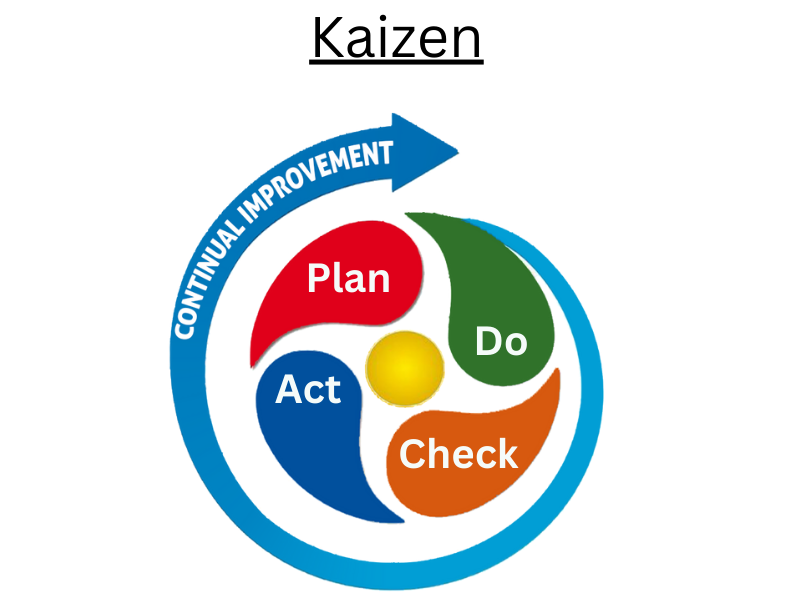
Kaizen or Continuous Improvement
What’s Kaizen?
- Kaizen stands for “ continous improvement” or “ small incremental advancements” of all areas of a company.
- Kaizen word comes from the Japanese words “ kai” which means “ change or enhancement” & “ zen” which means “ for betterment.”
- The lean tool Kaizen includes the involvement of all workers, from top management to bottom people.
Benefits of Kaizen
- It Improves processes by removing 7 type of waste from industries.
- Promotes growth of workers and the company.
- Kaizen Improves quality, safety, cost structures, delivery, Environment and it improves client service/ satisfaction.
How to apply Kaizen at our plant
The Kaizen system is generally enforced in 5 different way
- Identify an area having a problem.
- Analyzing the data and system for the current process system.
- Testing and assessing better possibility.
- Apply advancements.
- Analyzing results and present them to higher management for feedback.
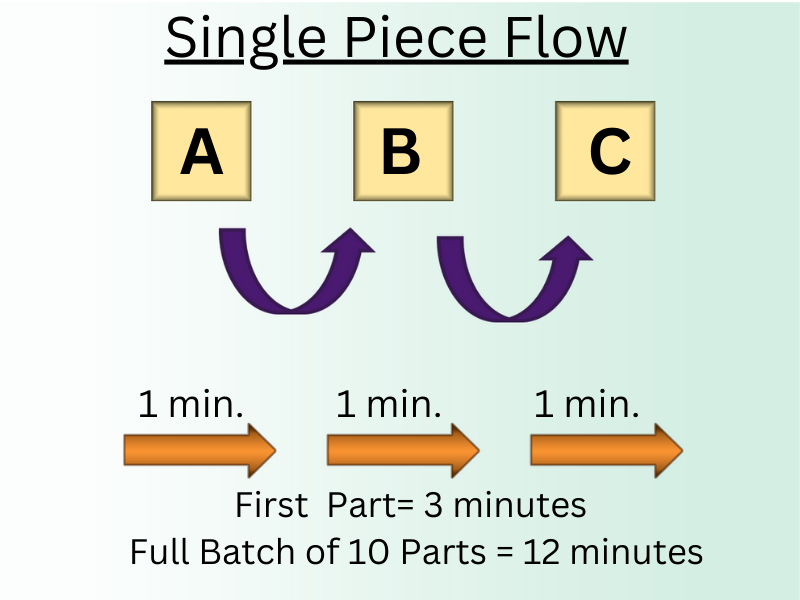
Single Piece Flow or One Piece Flow
What’s Single Piece Flow?
- Single Piece Flow is the sequence of a product or service through a process that’s the single unit is produced at a time.
- Single- Piece Flow is the opposite of batch product.
- In batch products, there’s a large number of products are prepared at a single time.
- Single- Piece Flow is concentrated on the manufacturing of the product itself rather than the waiting, transportation, and storehouse of the product.
Benefits of Single Piece Flow
- Single Piece Flow detects blights before and more accurate.
- In Single Piece inflow, we can get further flexibility for customization and meeting client demands.
- It reduces costs by barring colorful lean wastes.
- In Single Piece Flow we can fluently predict the delivery timing.
Jidoka (Autonomation)
What’s Jidoka (Autonomation)?
- Jidoka means Autonomation
- Autonomation described as” intelligent automation “or” automation with a personal touch”
- Jidoka (Autonomation) refers to incompletely automate manufacturing.
- Partial automation is generally much less precious than full automation.
- Jidoka implements some administrative functions rather than product functions.
- In this conception, the machine or line is automatically stopped when defect are detected.
Principles of Jidoka
The main principles of Jidoka are mentioned below.
- Defect the abnormality in the operation or product.
- Stop the operation or product.
- Fix or correct the immediate condition of the process or product.
- Investigating the root cause and install a countermeasure in process or product.
Benefits of Jidoka (Autonomation)
- Jidoka helps workers fix problems as they do.
- It improves productivity.
- Jidoka reduces downtime and breakdowns.
- It empowers workers and machines.
Poka- Yoke
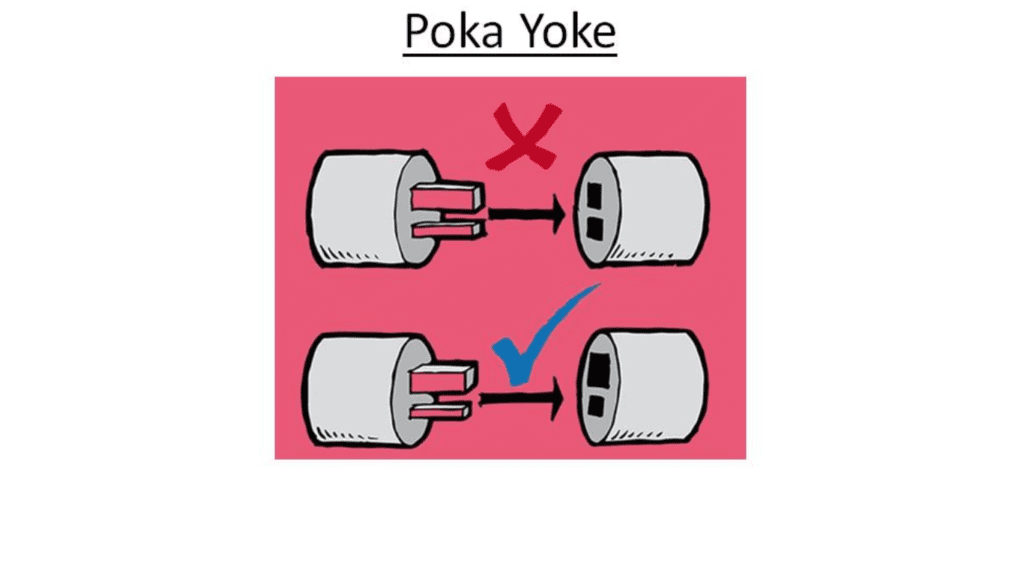
What’s Poka-Yoke?
- Poka- Yoke means Mistake Proofing or Error Prevention.
- Poka- Yoke prevents defect from being made or it highlights a defect so that it isn’t passed to the coming operation.
Benefits of Poka-Yoke
- Poka- Servitude saves time and money by prevent defect or being made imperfect products.
- It’s difficult to find all defect by examination so we can use Poka-Yoke for effective and efficiency operation.
- Poka- Yoke prevents mortal error and it’s a very important tool.
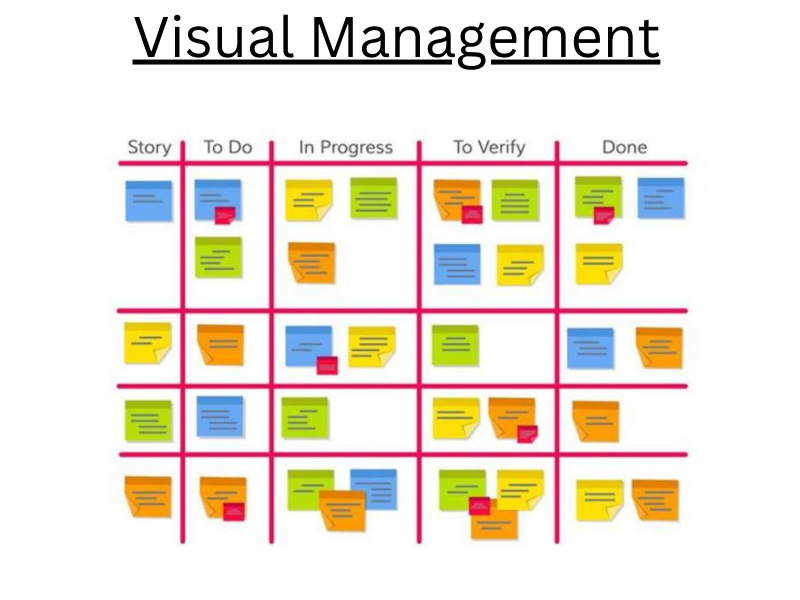
Visual Management
What’s Visual Management?
- Visual Management is a communication fashion that uses visual aids to pass note more effectively, more efficiently and very rapid.
- Visual Management is the ability to manage everything in your plant or areas by visually.
Benefits of Visual Management
- Visual management can display problems in a simpler way and veritably effective.
- Easily indicates our targets and goal.
- Visual management can increase the effectiveness of communication.
- Work instructions can be simplified by using the Visual Management Concept.
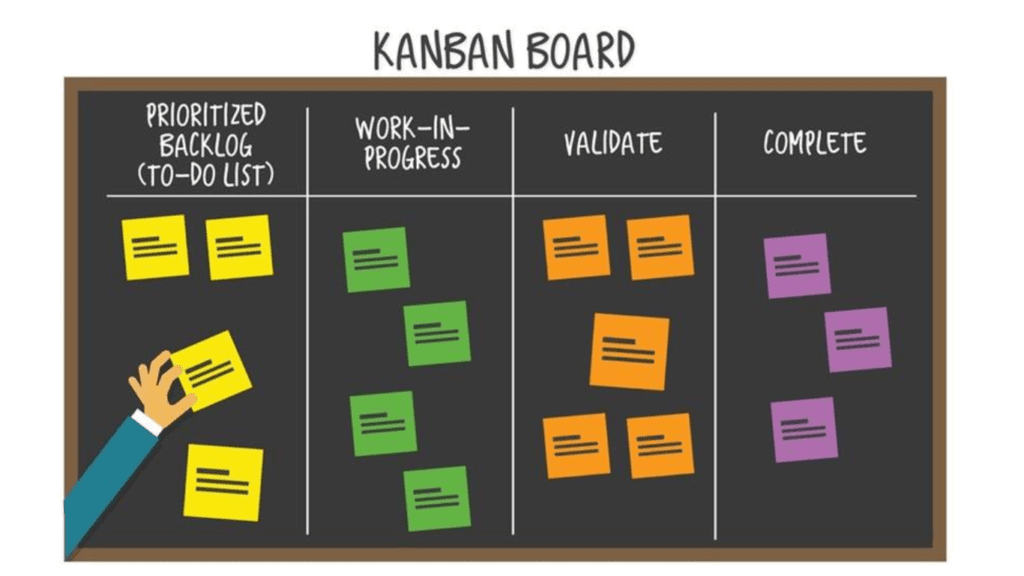
Kanban
What’s Kanban?
- Kanban means signboard or Billboard.
- Kanban is a scheduling system for lean manufacturing and just- in- time manufacturing (JIT).
- It takes its name from the cards that track production within a plant.
- Kanban controls the inventory position at any stage of production.
Benefits of Kanban
- Kanban improves manufacturing effectiveness
- One of the main benefits of kanban is to establish an upper limit to work in process inventory to avoid overcapacity
- Kanban is an effective tool to support the handling production system
- Kanban reduces wastes.
8 Lean Wastes
The 8 wastes in lean manufacturing are:
(1) Transportation waste
- Transportation is related to all unnecessary transportation condition within the association.
(2) Inventory waste
- Inventory waste is related to all finished goods and in- process goods which are kept by us on because of the forecast and it’s nonmoving.
(3) Motion waste
- Moving waste is related to people and equipment inefficiently moving between tasks.
(4) Waiting waste
- Waiting is how important time is consuming between your production step in ideal condition.
(5) Over Production waste
- Over Production is that we’re producing additional products than client’s demand.
(6) Over Processing waste
- We’re doing additional operations to finish good products for that client isn’t willing to pay.
(7) Defect waste
- The generation of defect in product is a total waste for that we’ve to spend on rework or repair or scrap.
(8) Skill sets (non-utilized talent) waste
- If we aren’t using our man force efficiently also that’s a waste.
Benefits of barring 8 Lean Wastes
- It increases productivity
- It creates a safer working environment
- Reduce downtime
- Improve efficiency and effectiveness
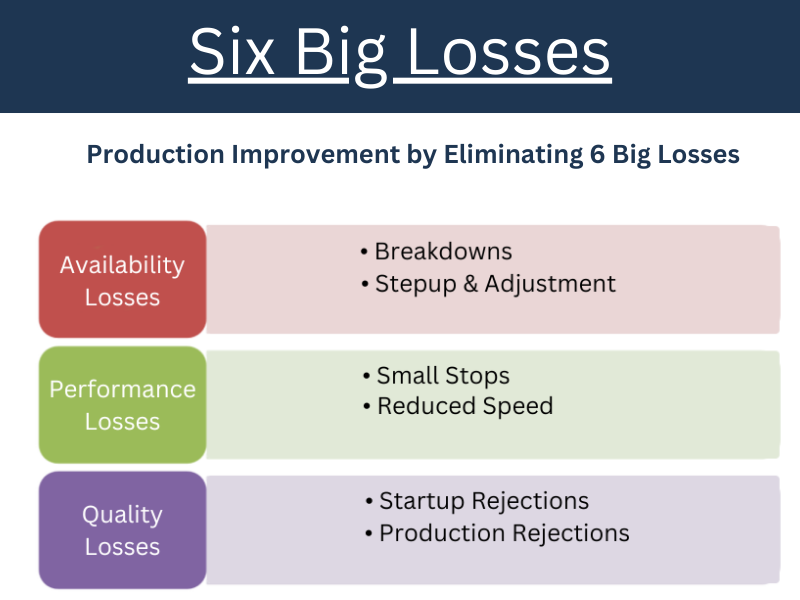
Six Big Losses
The six big losses are
(1) Breakdowns or Unplanned Stops
- It refers to mechanical failure and the need for preservation or suspension due to an unplanned task like force aren’t available.
(2) Planned Stops or Setup/ Adjustment
- Machines are stopped due to planned events, similar as planned preservation, safety examinations, or hand breaks and Setup/ Adjustment refers to transformation and machine warm-up.
(3) Small Stops or Idling
(4) Speed or Slow Cycles
- Small stops or Idling refers to machine stops for a short duration of time to correct settings, unclog logjams, and routine cleaning exertion.
- Speed or Slow Cycles are appertained to machine runs slower than designed, low effectiveness of operator and machine wear down.
(5) Production Rejects or Defect
- Production Rejects or defect are imperfect piece produced in the regular production, this is due to operator error or incorrect settings.
(6) Startup Rejects or Startup losses
- Startup Rejects or Startup losses are imperfect piece produced at the time of machine startups or during the operation or product transformation
Benefits of analysis of Six Big Losses.
- Six Big Losses provides us with a framework for remove the most common causes of waste in manufacturing.

SMART GOAL
What are SMART GOAL?
- The SMART Goal is the system to set the goal or target in an effective manner.
The goal should be easily defined and communicated.
The acronym SMART stands for
- S-Specific
- M-Measurable
- A-Attainable or Achievable
- R-Realistic or Results- Concentrated
- T- Time-bound
Heijunka
What’s Heijunka?
- Heijunka means Leveling or Balancing.
- It’s used to minimize batching and produce a more effective manufacturing process.
- It’s a type of product scheduling and it supports a predictable and steady flow of small- batch manufacturing, rather of larger product processes used for goods and factors.
Illustration of Heijunka
Say a auto manufacturer receives 1000 orders for buses every week. 200 on Monday, 100 on Tuesday, 100 on Wednesday, and 600 on Thursday. Rather of manufacturing 1000 buses at the morning of the week or the exact quantum demanded each day, the company would produce exactly 200 buses per day. By producing the same quantum every day, the plant can optimize the manufacturing operation for 200 buses and thus produce a more effective process.
Benefits of Heijunka
- Heijunka ( Leveling or Balancing) improves effectiveness at all situations of the manufacturing operation.
- It improves productivity and reduces the defect
- Heijunka reduces supplies, working capital costs, man force, and production lead time.
Just in Time
What’s Just in Time?
- It’s concentrated on the production of client’s demand like when they want it, how numerous amounts they want it, and where they want it?
- In this methodology, we produce the only client’s ordered volume rather of creating a large stock of a product.
Benefits
- It reduces unessestial force.
- Minimize the storehouse need and it gives companies flexibility in their manufacturing operations.
- Save unnecessary charges.
Takt Time
What’s Takt Time?
- It’s the maximum amount of time requires to produce the product and satisfy the client’s demand.
- It’s in other words Net time available to work per unit of client’s demand or Takt time (T) = Net time available to work (Ta)/ Demand ( client demand) (D)
- Where,
T = Takt time,
Ta = Net time available to work, e.g. ( working 8 hours per day)
D = Demand ( client demand),e.g. (units needed is 1000 qty per day)
Illustration
- If there are a aggregate of 8 hours (or 480 mins) in a shift ( gross time) lower 30 mins lunch, mins of tea breaks (2 × 10 mins), 10 mins for a meeting with platoon, also the net Available Time to Work = 480-30-20-10 = 420 mins.
- If client demand were 840 units per day and one shift was being run, also the line would be needed to affair at a minimal rate of two piece per nanosecond in order to satisfy the client’s demand.
Benefits
- It keeps track of production rates
- It helps us to set real- time targets for production and reduces gratuitous wastes.
- We can achieve a harmonious inflow of production by using takt time
- We can exclude the waste of overproduction by producing to meet actual client demand.
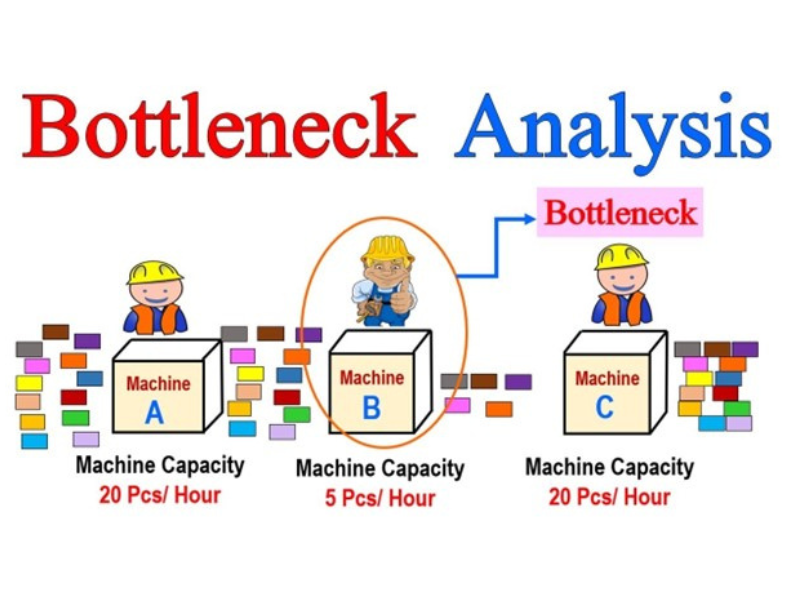
Bottleneck Analysis
What’s Bottleneck?
- A Bottleneck means” constraint”.
- The bottleneck in operation is understood by the stage of operation that takes the longest time in the whole operation
- The bottleneck refers to the slowest member of the whole operation or it can determine the speed of the entire group.
- If one part of the whole operation is slow, also it can reduce the speed of the whole operation.
- Also, it reduces the effectiveness of the entire manufacturing process.
Benefits of Bottleneck Analysis
- By removing bottleneck we can increase effectiveness and gains.
- We can optimize the cycle time.
- Increase productivity and factory capacity.
Andon
What’s Andon?
- Andon is a visual signaling system for the shop floor that indicates production status and cautions when backing is demanded
- Andon empowers drivers to stop the production process if any abnormity plant in product or process.
- Generally, Andon uses a combination of lights and sounds to communicate any problem, production status updates, highlight the issues, and any achievements.
Benefits of Andon
- Andon brings an immediate response to problems as they do
- It empowers operator
- Andon keeps the shop floor person engaged with their tasks
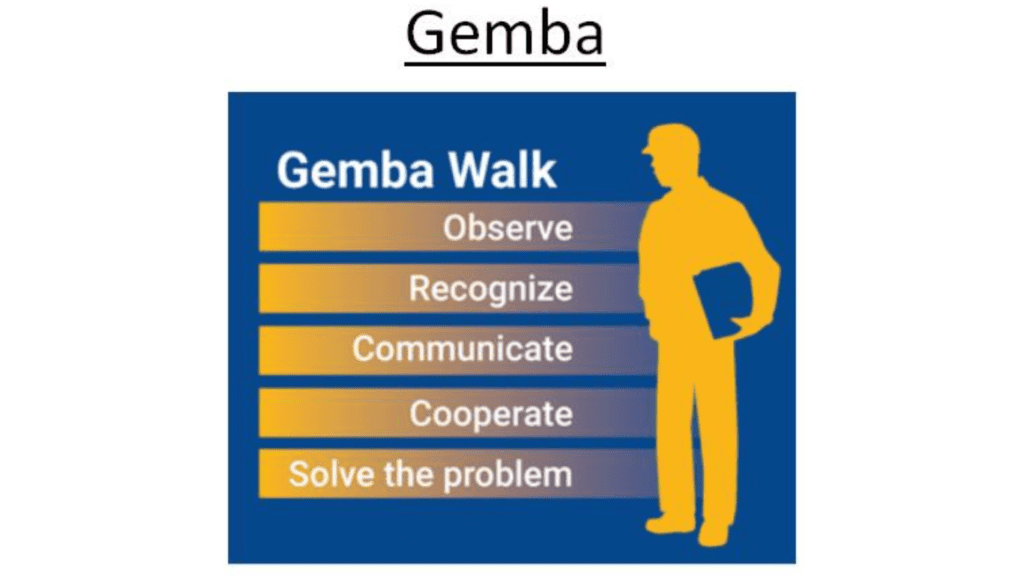
Gemba
What’s Gemba?
- Gemba is a Japanese word.
- Gemba means “The Real Place”.
- It means the actual place where the problem was plant or an incident has happed.
- As per Gemba theory, we must have to go at the Gemba for investigate of any problem or incident.
- So problem solver’s or Cross serve Team’s presence is necessary at Gemba.
- The actual place may be appertained In manufacturing, it’s a shop floor or it can be a construction place, assembly line, any lab, office, etc.
Basic Principles of Gemba Walk
Basic Principles of Gemba Walk are mentioned below
- Have a specific purpose of Gemba Walk.
- Be familiar with the area that you’re visiting.
- Understand the overall process.
- Rightly understand what you’re seeing.
- Know what to ask.
Benefits of Gemba
- By Gemba walk, we can get fluently knowledge of the factory’s productivity.
- Gemba gives a deep, thorough, and effective understanding of the manufacturing process and problems by observation and conversations with shop floor workers.
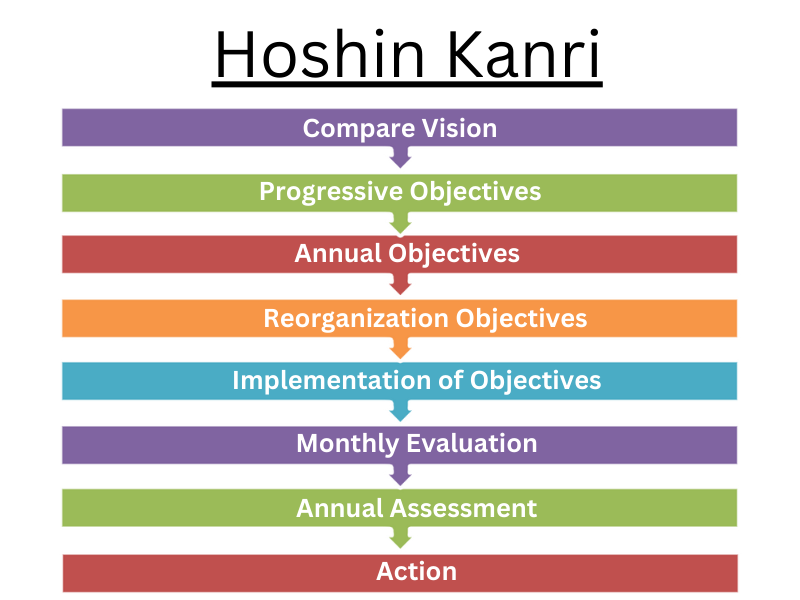
Hoshin Kanri
What’s Hoshin Kanri?
- Hoshin Kanri is a Japanese Word it means Policy Deployment
- The word “hoshin” means direction.
- And The word “kanri” means administration.
- In Hoshin Kanri, the strategic pretensions of the company are communicated throughout the company and also put into action with the help of middle operation.
- The top-down approach focus on steady communication for explaining fancies, developing and enforcing policy from top to nethermost operation, and entering feedback from bottom to top operation.
Benefits of Hoshin Kanri
- The Hoshin Kanri practice helps us to insure that all workers within an association are suitable to understand the association’s vision.
- And all workers work toward a common thing of an association.
- It eliminates the waste that comes from poor communication and an unorganized direction.
Overall Outfit Effectiveness (OEE)
What’s Overall Outfit Effectiveness (OEE)?
- OEE is a system used to measure manufacturing effectiveness by using Performance Rate, Vacuity of Machine and Quality Rate.
- It measures the effectiveness of Productivity in.
- With 0 means zero productivity it means an hamstrung product.
- 100 OEE means perfect product ( produced only good corridor, as presto as possible, with no time-out).
- OEE is calculated with the formula,
- OEE = ( Vacuity) * ( Performance) * (Quality)
Benefits of OEE
- Knowing OEE helps us to find inefficiencies in the product cycle.
- It helps us to set pretensions for enhancement, and track the progress.
- OEE provides standard data for the new process setup.
- OEE helps to track progress in barring waste from a manufacturing process.
Cellular Manufacturing
What’s Cellular Manufacturing?
- Cellular Manufacturing is creating process inflow by dividing the full process into small sub-processes or way.
- This small sub-processes or way are called cells.
- By combining these cells are called cellular manufacturing.
- In Cellular Manufacturing the analogous products are produced in the same cell.
- The product moves through the whole process without any cessation or any interruptions.
- Generally the cells are arranged in a “U-shape” design, this design allows a administrator to move less and have further watch over the entire process.
Benefits of Cellular Manufacturing
- Cellular Manufacturing improves productivity and affair
- Cellular Manufacturing reduces rejection and optimizes the bottom space.
- Quick change over possible
- We can make a wide range of analogous products in a single line.
- Reduce super eminent time.
- Enhance cooperation and communication between workers.
Total Productive Conservation (TPM)
What’s Total Productive Conservation?
- TPM is a well- defined system of maintaining and perfecting the product system and quality systems between the processes, machines, workers, outfit, and processes.
- TPM adds business value to an association.
- Total Productive Conservation (TPM)
focuses on visionary and precautionary conservation to maximize the functional time of outfit and reduce outfit failure rate as much as possible in order to increase product effectiveness. - TPM fully removes the difference between product and conservation by strong focuses on empowering drivers to maintain their own outfit.
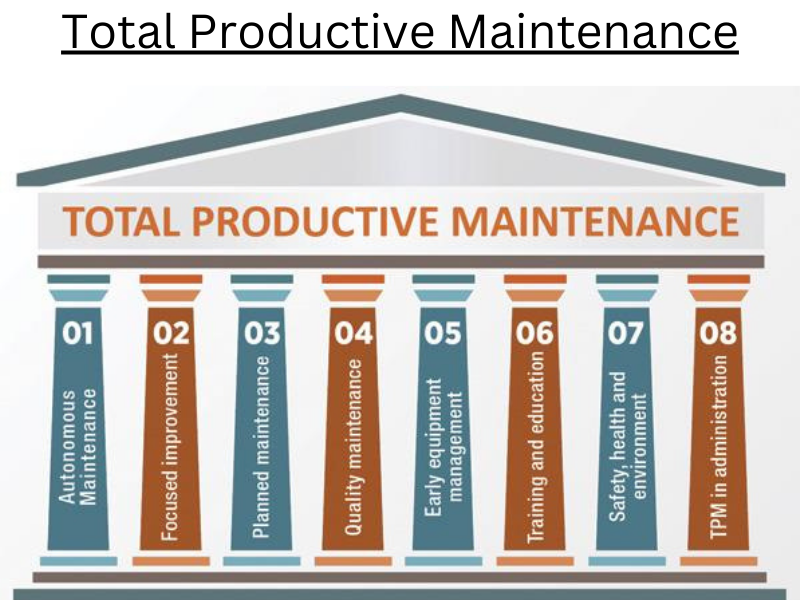
The Eight Pillars of TPM
- Autonomous Conservation
- Concentrated Enhancement
- Planned Conservation
- Quality operation
- Early/ outfit operation
- Education and Training
- Executive & office TPM
- Safety Health Environment
Benefits of Total Productive Conservation (TPM)
- TPM Reduces time-out and increases productivity
- It Improves Quality
- It creates a safer working terrain
- TPM Enhance cooperation and communication between workers and empower the drivers
Total Quality Management (TQM)
What’s Total Quality Management?
- Total Quality Management is a client- acquainted process and it focuses on nonstop enhancement of Product, Process or Service of an association.
- The thing of Total Quality Management (TQM) is to increase the quality at every single step in an association.
The Principles of Total Quality Management
- Focus on client
- Hand involvement
- Process- centered
- Integrated system
- A strategic and methodical approach
- Decision- making grounded on data
- Communication
- Nonstop enhancement
Benefits of Total Quality Management
- Total Quality Management (TQM) will increase the mindfulness of quality within the association.
- TQM establishes a quality- acquainted culture within the association
- TQM emphasis on cooperation.
- It’ll increase commitment towards nonstop enhancement within the association.
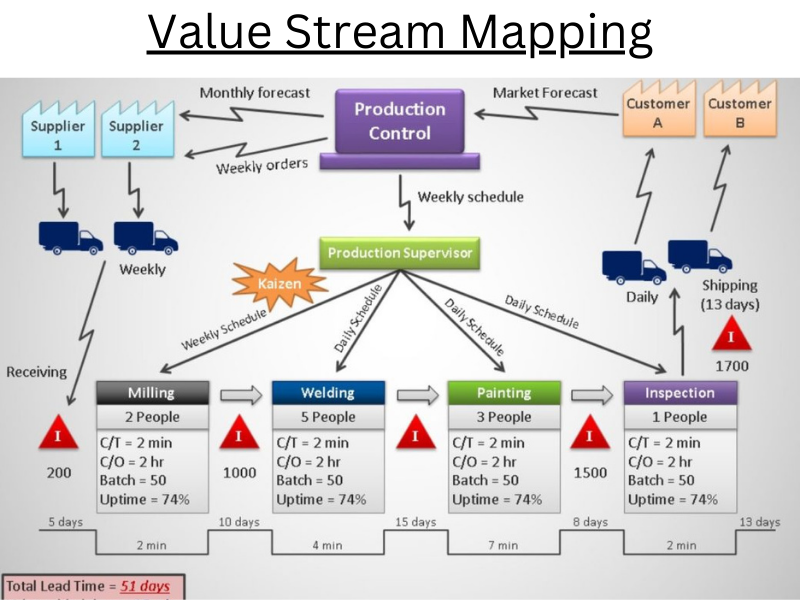
Value Stream Mapping
What’s Value Stream Mapping?
- Value Stream Mapping is a system of assaying the current state of a process and designs the unborn state of the process and it focuses on the occasion for enhancement by barring different wastes from processs.
- Value Stream Mapping includes the process, from the supplier end to reach at the client end.
- The process inflow illustration is used to identify the waste and inefficiencies from the process in Value Stream Mapping.
Main Three Parts of Value Stream Mapping are
- Map Current State ( Identify Waste)
- Design Unborn State
- Produce a Transformation Plan
Some common data collection points for Value Stream Mapping are
- The time is taken by one product or to pass one product from one station to the coming station
- Position of Force
- Number of drivers
- A number of shifts worked
- Batch size
- Change over and delivery time
- Productivity etc.
Benefits of Value Stream Mapping
- Value Stream Mapping addresses underpinning issues.
- It helps to identify wastes and exclude wastes.
- Value Stream Mapping helps to identify inefficiencies in the process.
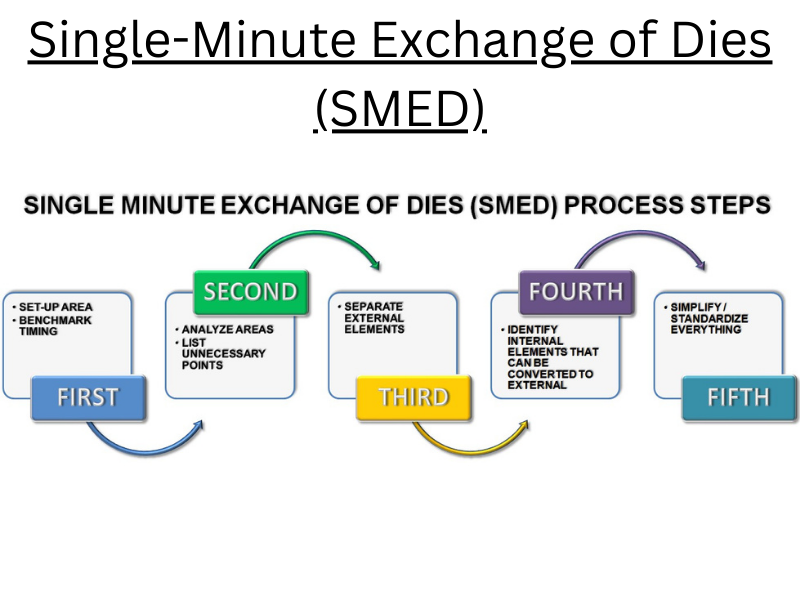
Single-Minute Exchange of Dies (SMED)
What’s the Single-Minute Exchange of Dies (SMED)?
- Single-Minute Exchange of Die (SMED) is a system for reducing setup or change overtime in a manufacturing process to lower than 10 twinkles.
- The effectiveness of the operation or process can ameliorate by reducing the setup or transfiguration time in the plant.
- The conception of SMED was given by Frederick Taylor in 1911 and it was used by Ford Motors in 1915.
Principles of the Single-Minute Exchange of Dies (SMED)?
- Identify transfiguration tasks.
- Dissect each task to determine the purpose.
- Determine low- cost results.
- Apply that result to reduce the transfiguration time.
Benefits of Single-Minute Exchange of Dies (SMED)
- SMED improves effectiveness
- SMED improves productivity
- It gives further inflexibility to product.
- With the help of SMED, we can reduce force and enable a advanced rate of product.
Crucial Performance Pointers (KPIs)
What are KPIs?
- KPIs are essential criteria set by the operation in order to check the success of spare manufacturing pretensions or performance of any process.
- Crucial Performance Pointers (KPI) are important for measuring effectiveness, waste, and productivity.
Exemplifications of common manufacturing KPIs are
- Speed
- Count
- Cost of Poor Quality
- Reject rate
- Client Satisfaction Indicator or standing
- MTBF, MTTR., etc.
Benefits of KPIs
- It helps to ameliorate effectiveness and productivity
- It helps operation to define the places and responsibility of workers
- Produce a vision, charge, and pretensions of an association
- It helps to set objects and targets
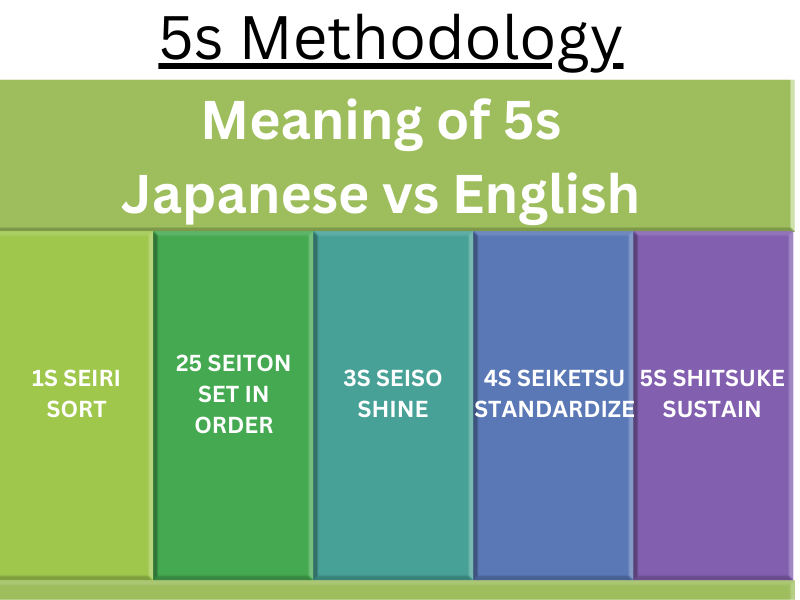
What’s 5S Methodology?
5S Methodology is a system for organizing spaces so work can be performed effectively & efficiently with safely.
5S Meaning
- (S1) Seiri → Sort
- (S2) Seiton → Set In Order
- (S3) Seiso → Shine or Clean
- (S4) Seiketsu → Standardize
- (S5) Shitsuke → Sustain
Benefits of 5S Methodology
- Increase productivity through effectiveness
- Reduction in detainments
- Advanced Quality
- Ameliorate in Safety
- Set-up times reduced
- Morale & Provocation Increase
- Lower stress for drivers
- Safer work terrain
Formalized Work

What’s the Formalized Work?
- The standardized work is proved procedures for any process.
- It must be a live document so that it can be fluently changed as per the revision of the process.
Benefits of Formalized Work
- More attestation of current operation inflow.
- Formalized Work helps to train the driver.
- Enhancement in productivity and gains.
- Reduces variation in the operation inflow.
- It adds discipline towards a work.
- Formalized Work promotes problem- working.
- Regularize Work Increases cooperation across the association.
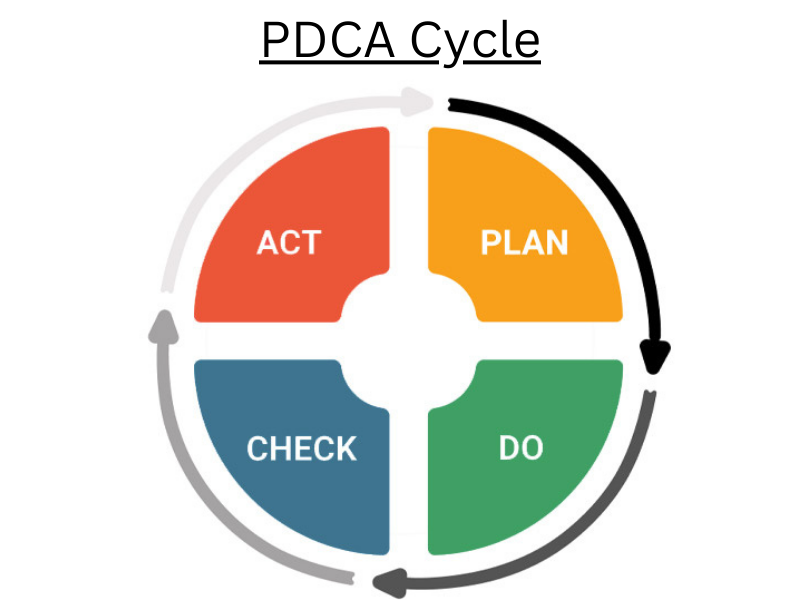
PDCA Cycle
What’s the PDCA cycle?
- The PDCA Cycle is the Plan- Do- Check- Act Cycle.
- PDCA is a well-defined problem working system
and nonstop enhancement.
The way in the PDCA cycle is
(1) Plan
- The problem is linked and all workers work together to develop a plan for making improvements or working on the linked problem.
(2) Do
- The plan is enforced as per the defined result by across-functional platoons.
(3) Check
- Check the enforced result and also bandy further advancements that can be possible or not.
(4) Act
- The enforced result is proved if it has successfully answered the original problem.
- And If the result isn’t satisfactory also again the cycle starts over at the Plan phase for chancing out other factors.
Benefits of the PDCA Cycle ( Plan- Do- Check- Act Cycle)
- It helps to apply Kaizen and other nonstop enhancement conditioning.
- PDCA system Improves the brainstorming chops of your platoon