In a world driven by continuous improvement and efficiency, problem-solving is a skill that holds immense value. Whether you are a professional in the corporate realm or an individual looking to enhance your critical thinking abilities, understanding and implementing structured problem-solving methodologies is crucial.
One such powerful approach is the 8D problem-solving methodology. In this comprehensive guide, we will delve into the intricacies of the 8D methodology, dissecting each step, and uncovering how it can be your secret weapon in tackling complex issues effectively.
What’s 8D Methodology?
- 8D Methodology is a methodical problem-solving tool or you can say it’s a strategy.
- It was made popular by “The Ford Motor Company” in the automotive industry. And now it has been widely used by many organisations across the globe
- These are 8 disciplines 8 steps that must be followed for identifying and barring a problem in a product, process, or service.
Eight steps of Problem Solving
- Establish the team
- Describe the problem
- Develop interim containment actions
- Define and validate root cause & escape points
- Choose and validate endless corrective actions
- Implement and validate endless corrective actions
- System prevention actions to help a recurrence
- Fete team contributions
Step - 1 Establish the Team
- Purpose
- Establish a small group of people with applicable knowledge.
- Key activities of the team in step 1
- Review priorities, scope, and problem
- Identify how big a team is demanded
- Identify team members and establish the team
- Nominate a team leader, project champion and facilitator Assign the places and liabilities
Step - 2 Describe the Problem
Purpose of STEP 2
- Describe the internal or external issue by relating “ what is wrong with what” and detailing the problem in quantifiable terms so it’s easy to take more action.
Key exercise in STEP 2
- Develop a problem statement and a flowchart of all operation steps and identify critical operation steps with respect to the problem.
- Establish a high-level project plan, including milestones, project goals, and objects.
- The description should define the boundaries.
We can use the below tools to describe the problem.
- 5W2H strategy
- Why-Why Analysis
- Check Sheet
STEP - 3 Develop Interim Containment Actions
Purpose of STEP 3
- Define, validate and apply interim containment action to insulate the effects of the problem from any internal and/ or external client until permanent corrective (preventative) conduct is enforced.
Key activities in STEP 3
- Define the interim containment action
- Verify the effectiveness of the interim containment action
- Select and apply interim constraint action
- Validate the effectiveness of implemented interim containment action with the client
The containment actions must be enforced at the below position
- Client’s finished good (FG) warehouse
- At the client’s line
- Client’s RM warehouse
- Supplier’s FG warehouse
- At the Supplier’s line
- Supplier’s RM warehouse
- Also, check at sub supplier’s sequence of operation
We can use the below tools for developing interim containment actions
- Why-Why Analysis
- Check Sheet
- Process Flow Diagram
STEP - 4 Define and validate Root Cause & Escape Points
Purpose of STEP 4
- In this stage, the root cause is linked to taking permanent action to exclude the problem.
Key exercise in STEP 4
- Development and verification of root cause through data collection
- Review process flow for the place of the root cause
- Determine the escape point
- The escape point is the closest point in the process where the root cause could have been plant but was not.
We can use the below tools for define & validate the root cause & escape points
- Fishbone or Ishikawa illustration
- Why-Why Analysis
- Check Sheet
- scattering Diagram
- Process Flow Chart
STEP - 5 Choose and Verify Endless Corrective Actions
Purpose of STEP 5
- Select the best permanent corrective conduct to eliminate the root cause in the process.
Key conditioning in STEP 5
- Develop and select the result to remove the root cause & escape point
- validate that effectiveness of the selected results
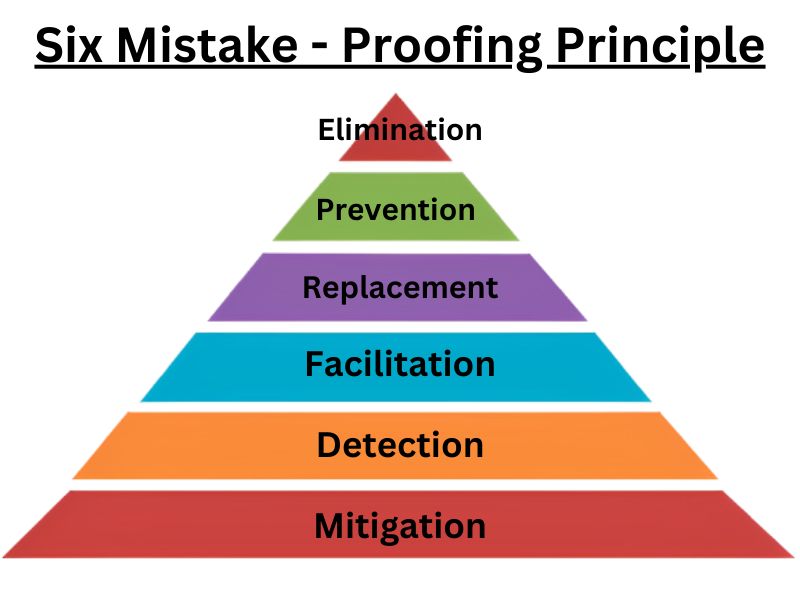
Six Mistake-Proofing Principles
- Elimination
- Prevention
- Replacement
- Facilitation
- Detection
- Mitigation
Several Mistake-Proofing techniques
- Variation Control
- Workplace Organization
- Identification ⇢Process Checks
- Poka-Yoke Devices
Various Mistake-Proofing Devices
- Guide Pins
- Error Detection & Alarms
- Limit Switches
- Sensors
- Vision Systems
- Counters& Timers
- Checklists
We can use below tools for Choose and validate Permanent Corrective Actions
- Fishbone or Ishikawa illustration
- Why-Why Analysis
- CheckSheet
- scattering diagram
- process flow Chart
- PFMEA ( ProcessFailure Mode and Effect Analysis)
- ControlPlan
STEP - 6 Implement and Validate Permanent Corrective Actions
Purpose of STEP 6
- Planand implement selected Permanent Corrective Actions
Key activities in STEP 6
- Implement the best result to remove the root cause & escape point
- Validatethe effectiveness of the implemented action.
- Monitorthe effectiveness of the enforced results and assure that they don’t cause any undesirable effects.
- Communicatethe plan to all applicable interested parties.
We can use below tools for apply and validate endless corrective actions
- Causeand Effect Diagram or Fishbone
- Why-Why Analysis
- CheckSheet
- scattering diagram
- process flow Diagram
STEP - 7 System Prevention Action to Prevent Recurrence
Purpose of STEP 7
- The purposeof the prevent recurrence is to partake the knowledge, preventing problems on similar products, processes, places or families.
Key exercise in STEP 7
- Reviewsimilar products and processes for problem prevention (Horizontal Deployment)
- To updateprocedures and work instructions
- AssurePFD, PFMEA and Control Plan have been updated
- Checkthe demanding standardization has been identified and implemented.
We can use below tools/ documents to prevent rush
- Cause& Effect Diagram or Fishbone
- Why-Why Analysis
- CheckSheet
- scattering diagram
- PFD ( ProcessFlow Diagram)
- PFMEA ( ProcessFailure Mode and Effect Analysis)
- ControlPlan
- WorkInstruction/ Bribe and Procedure
STEP - 8 Recognize Team Contributions
Purpose of STEP 8
- Identifythe lesson (s) learned and celebrating the success of the team.
Key exercise in STEP 8
- Performa final review of the problem- solving project
- Preparethe report for future reference
- Documentthe lesson learned
- Before and after comparison of issue
- Recognizethe team’s success and individual contributions
We can use below reports for the final stage in the 8D Methodology
- 8D Report
- lesson learned Report
- Before and After Comparison of the issue